Presentations
Posters

Choi, J., Lee, Y., Kim, B., Kim, H., and Noh, S. J.
Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2025)
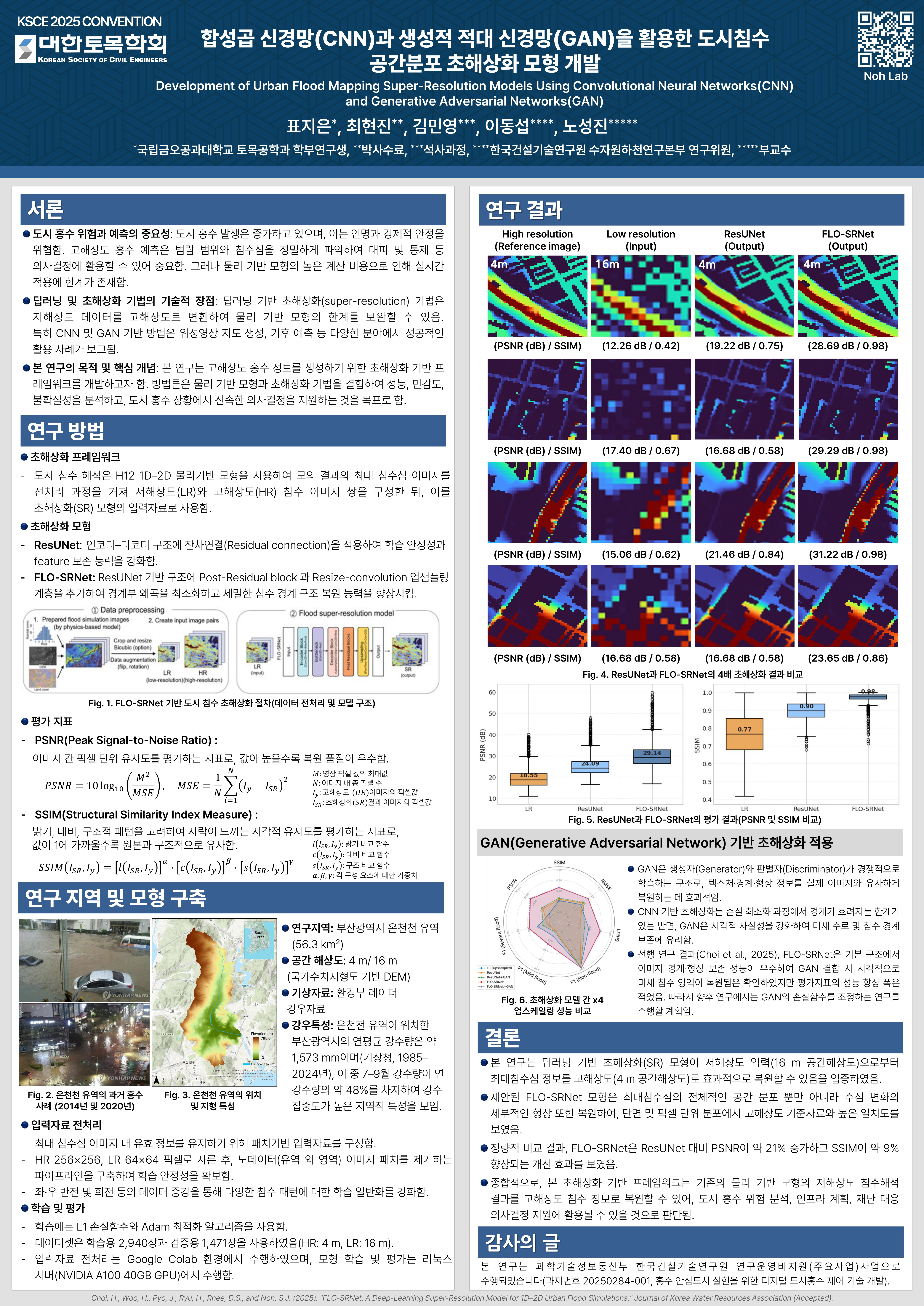
Pyo, J., Choi, H., Kim, M., Lee, D., and Noh, S. J.
Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2025)
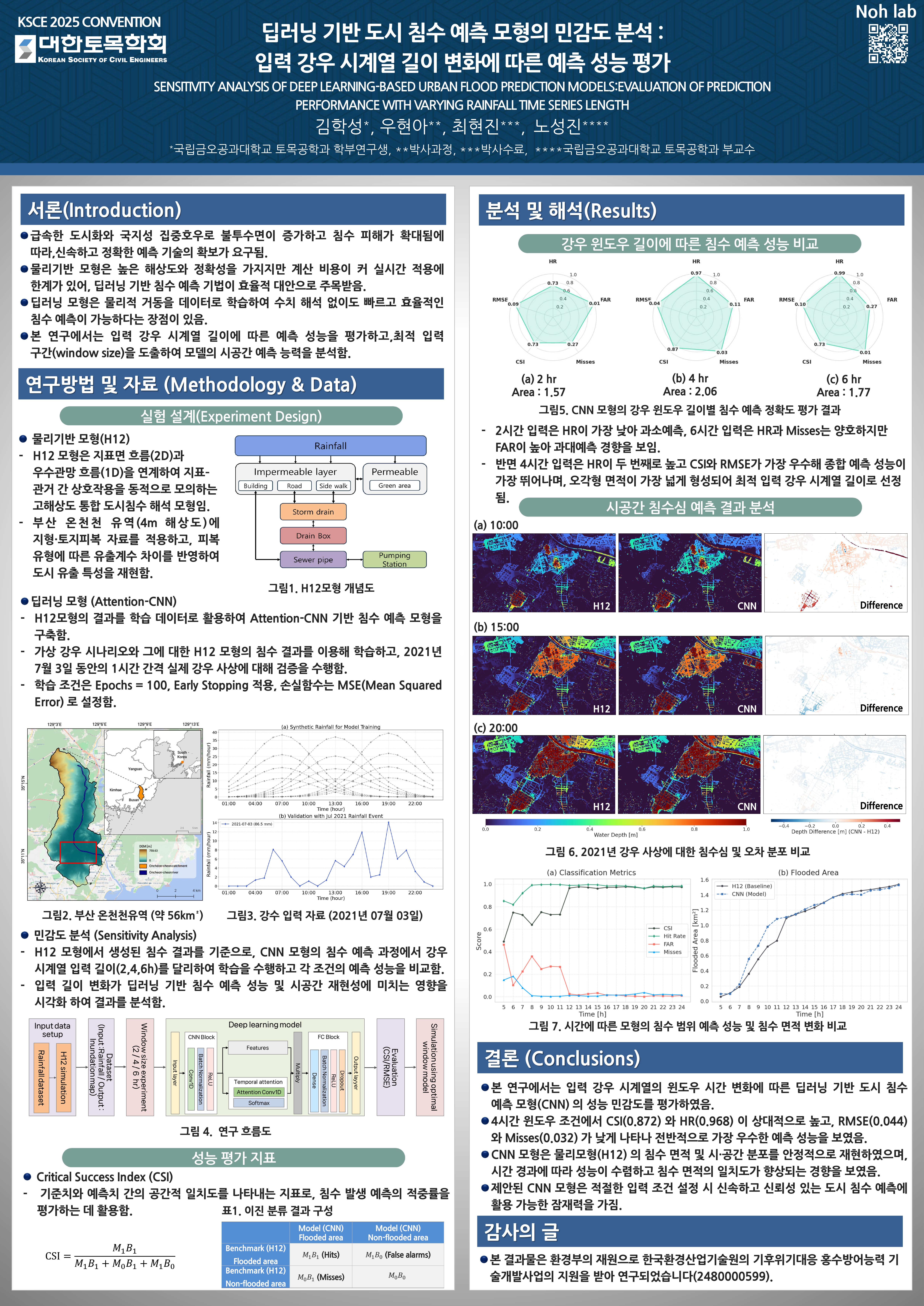
Kim, H., Woo, H., Choi, H., and Noh, S. J.
Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2025)

Han, S., Kim, B., Lee, Y., and Noh, S. J.
Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2025)

Jeong, D., Woo, H., Kim, M., Kim, B., and Noh, S. J.
Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2025)

Kim, H., Han, S., Choi, J., Woo, H., Choi, H., and Noh, S. J.
Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2025)
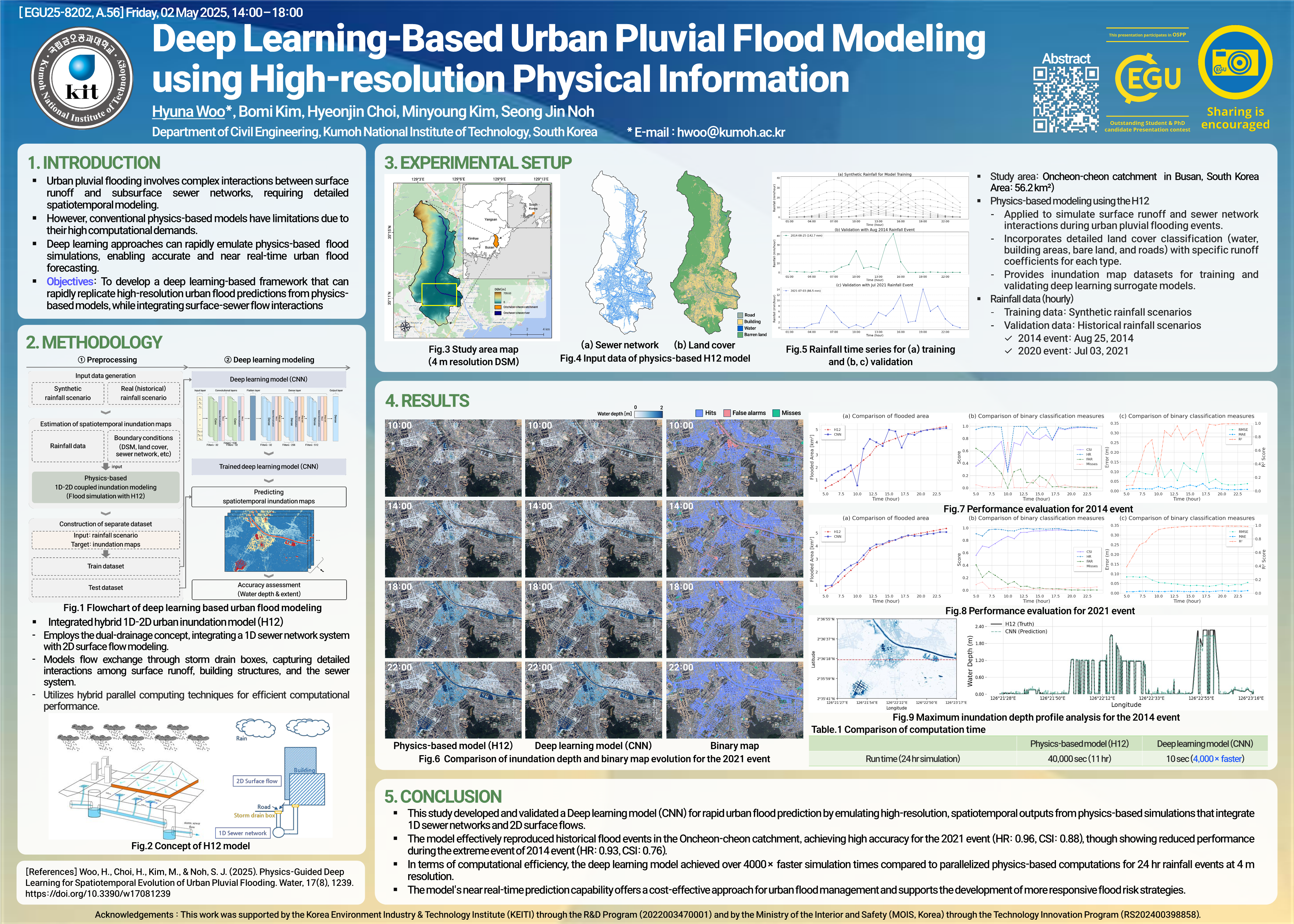
Woo, H., Kim, B., Choi, H., Kim, M., and Noh, S. J.
European Geosciences Union (2025)

Kim, B., Lee, Y., Lee, S., and Noh, S. J.
European Geosciences Union (2025)
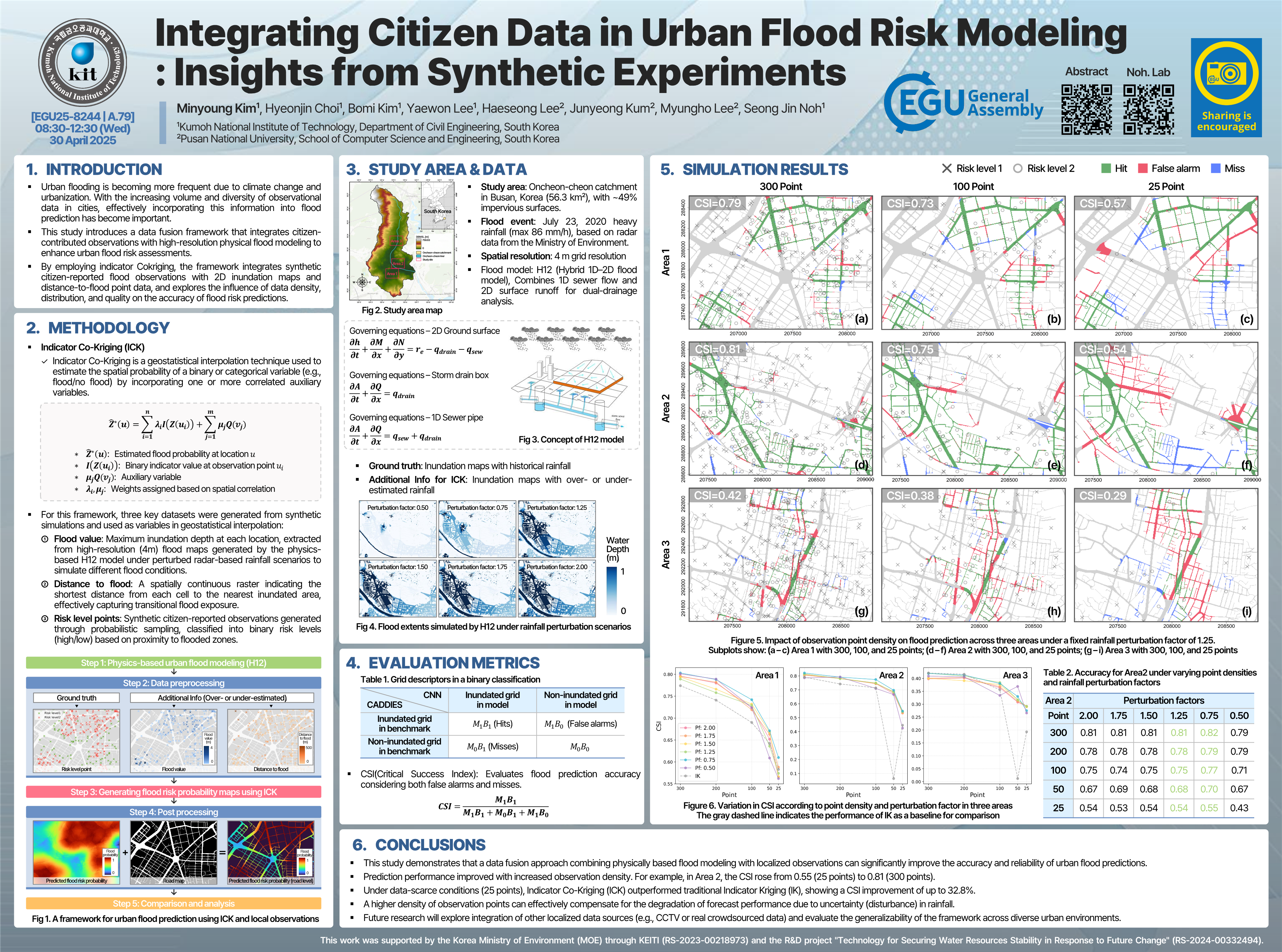
Kim, M., Choi, H., Kim, B., Lee, Y., Lee, H., Kum, J., Lee, M., and Noh, S. J.
European Geosciences Union (2025)
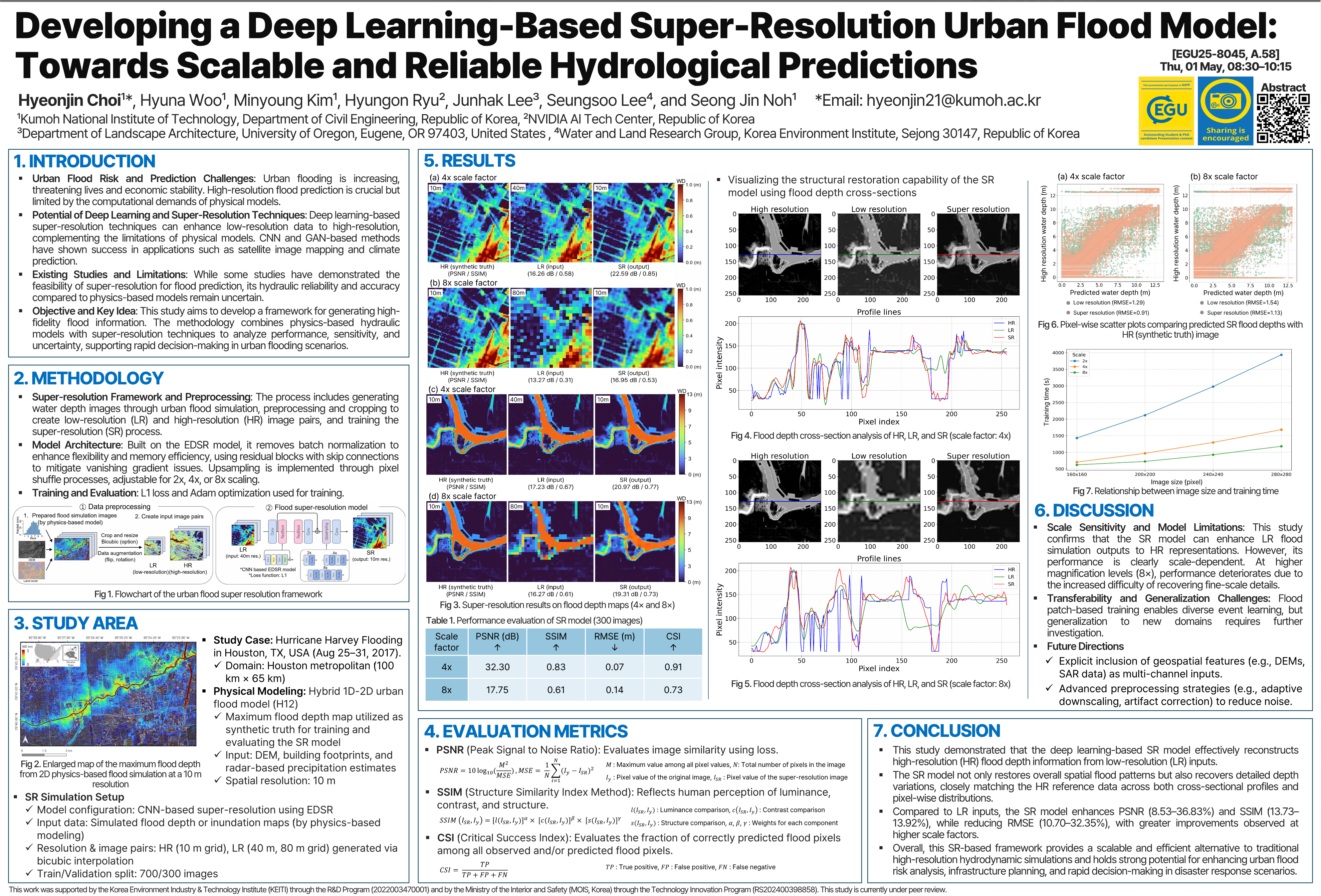
Choi, H., Woo, H., Kim, M., Ryu, H., Lee, J., Lee, S., and Noh, S. J.
European Geosciences Union (2025)
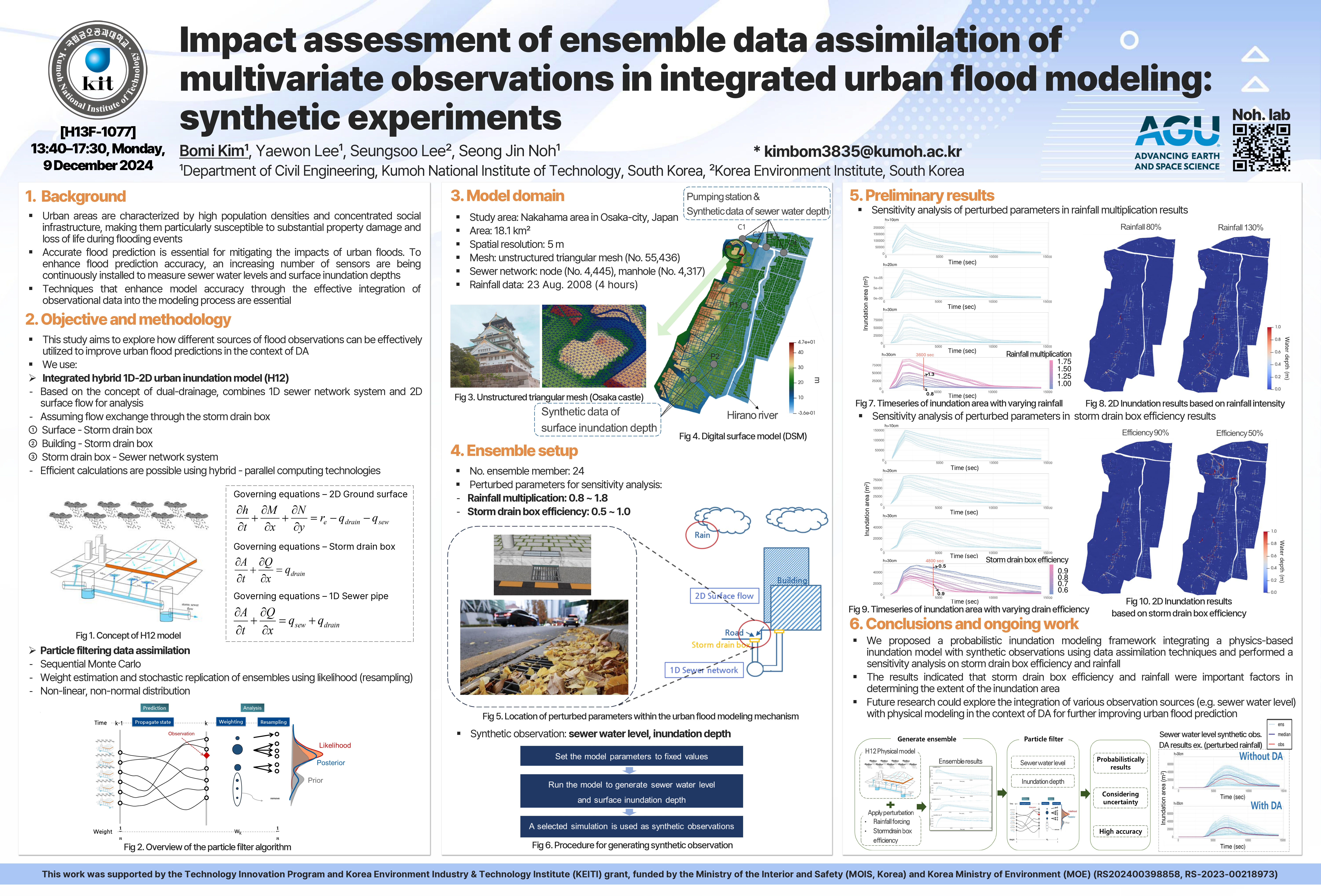
Kim, B., Lee, Y., Lee, S., and Noh, S. J.
American Geophysical Union (2024)

Kim, M., Woo, H., Choi, H., Kim, B., Lee, Y., Lee, S., Lee, J., and Noh, S. J.
American Geophysical Union (2024)
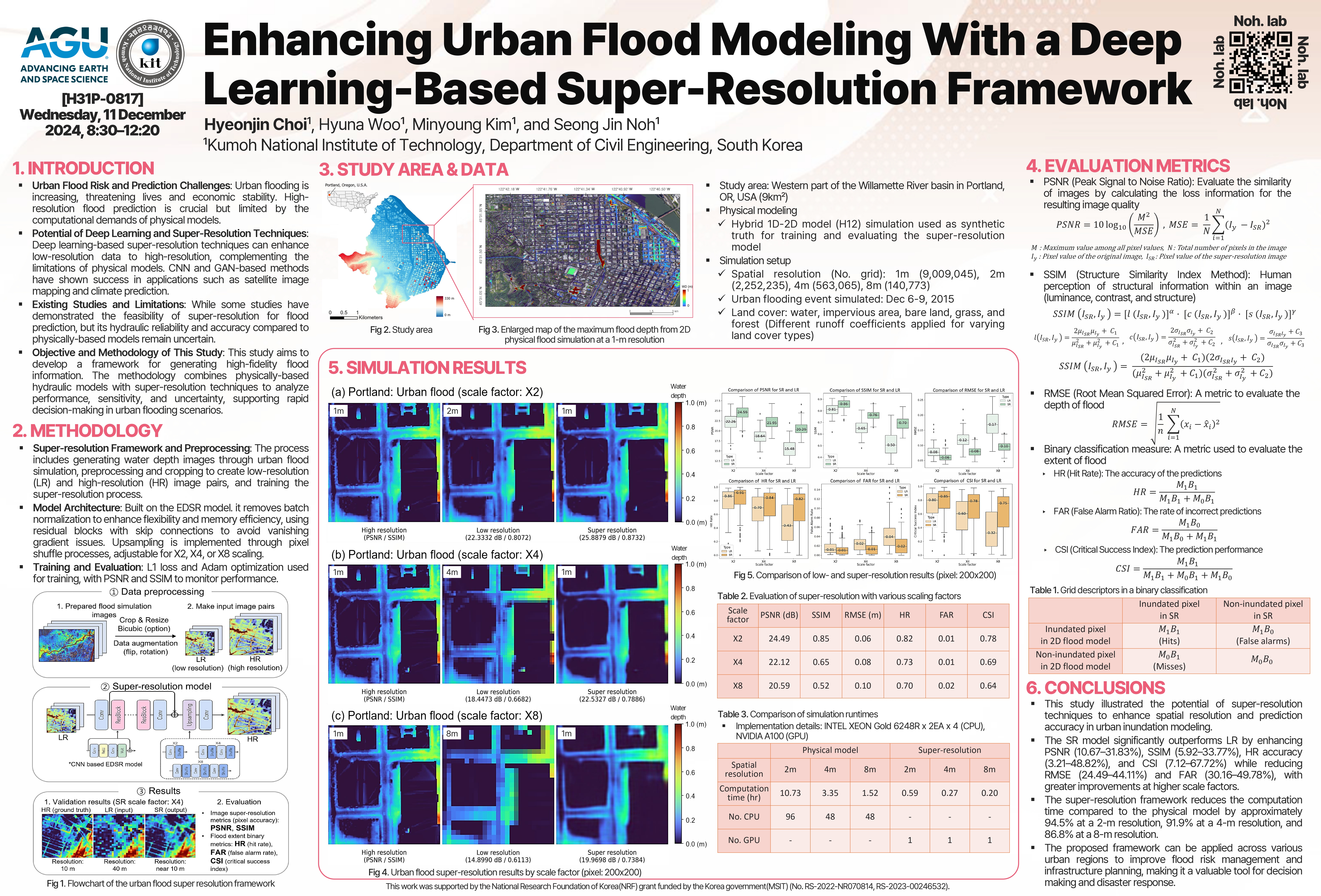
Choi, H., Woo, H., Kim, M., and Noh, S. J.
American Geophysical Union (2024)

Noh,S., Choi, H., Kim, M., Kim, B., Lee, Y., Kum, J., and Lee, M. H.
American Geophysical Union (2024)

Lee, Y., Kim, B., and Noh, S. J.
Asia Oceania Geosciences Society (2024)
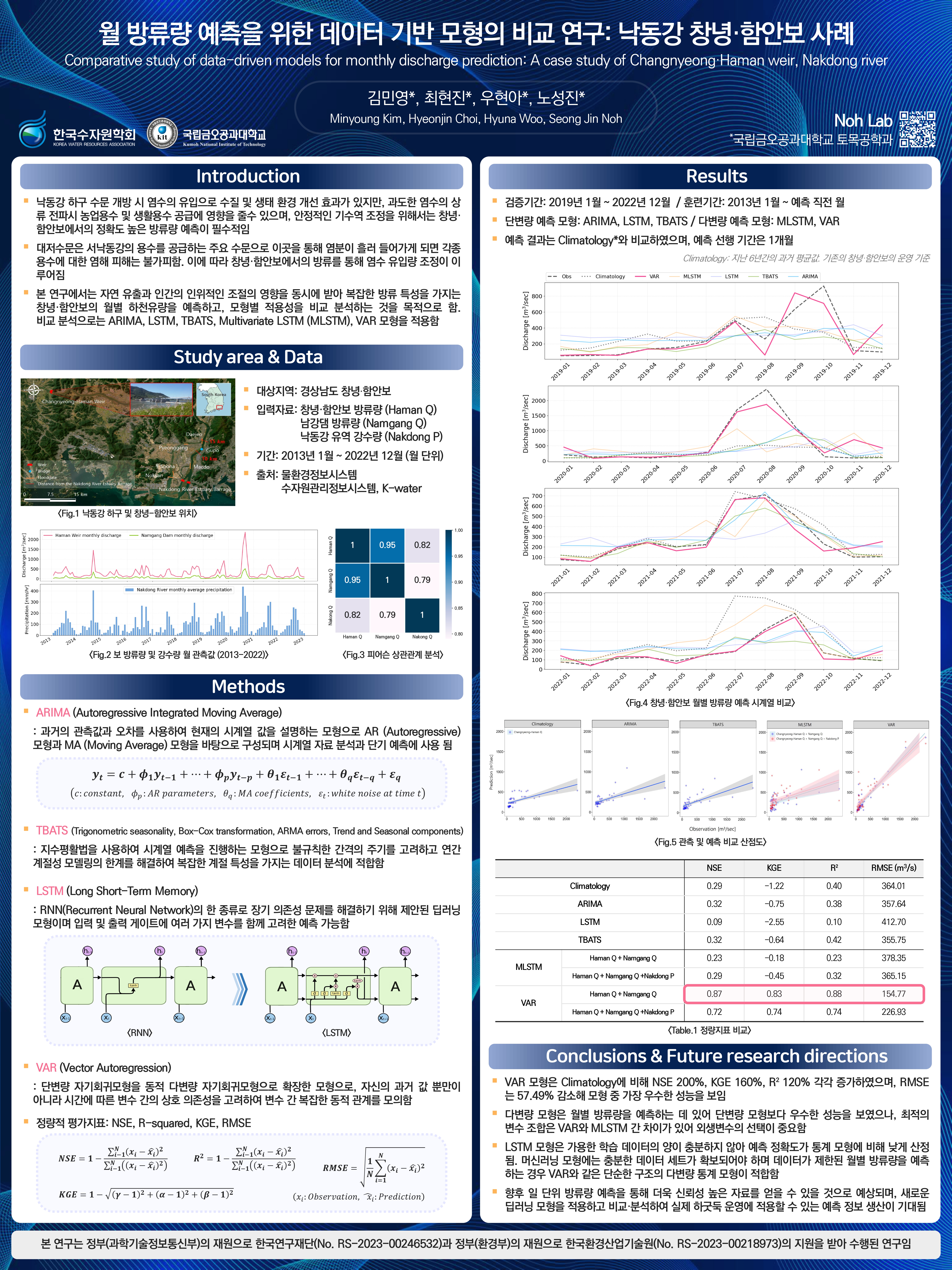
We compare data-driven models integrating meteorological and hydrological variables to optimally predict monthly outflow from river weirs influenced by natural runoff and human regulation, enhancing long-term operational decision accuracy for reliable water resources management.
Kim, M., Choi, H., Woo, H., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2024)

We introduce GEOGloWS, a global streamflow forecasting system, and analyze its streamflow predictions against observed data.
Choi, J., Choi, H., Kim, B., Lee, Y., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2024)

We develop an integrated CA-based flood model, including an stable inundation and infiltration process, and implement a CA-based model in downtown Portland, U.S. as a high-resolution pluvial flood simulation.
Choi, H., Lee, S., Woo, H., and Noh, S. J.
Asia Oceania Geosciences Society (2023)

We analyzed two ensemble-based sequential DA techniques, Ensemble Kalman Filter and Particle Filter, for stream flow prediction by a pumped hydrostatic model using airGRdatassim, and discussed the effect of DA-related hyperparameters on performance and ensemble distribution.
Lee, G., Kim, B., Lee, S., and Noh, S. J.
Asia Oceania Geosciences Society (2023)

We develope a system that effectively optimizes high-resolution WRF-Hydro model with limited information data using PEST technique and discuss challenges and solutions for sensitivity and uncertainty analysis to calibrate distributed hydrologic models.
Kim, B., Lee, G., Kim, S., Lee, Y., and Noh, S. J.
Asia Oceania Geosciences Society (2023)

In this study, the developed CA-Urban model is introduced, and the effect of Horton’s coefficient on infiltration according to soil characteristics and the spatial distribution of various land cover types on urban inundation and water cycle are analyzed.
Lee, S., Choi, H., Woo, H., Noh, S. J., and Kim, S. H.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2023)

This study analyzed the data collected for about a year in real time from soil observation equipment and weather observation equipment installed at Kumoh Institute of Technology and developed a prediction model based on machine learning technology.
Woo, H., Lee, Y., Choi, H., Kim, M., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2023)

Based on the distributed hydrological analysis model WRF-Hydro, a high-resolution water cycle and heat cycle model was constructed for the Geumho River basin to analyze the hydrological element analysis results.
Kim, S., Kim, B., Lee, G., Lee, Y., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2023)

Based on climate change scenarios, we analyze the impact of climate change on water resource management of multi-purpose dams, and propose a methodology that simultaneously analyzes water supply and flood risk during drought.
Noh, S. J., Woo, D. K., Jo, J., Lee, G., Lee, S.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2023)

The effect of spatial resolution of numerical surface data (DSM) on urban flooding analysis was analyzed by solving the vibration problem of CA-Urban model using cellular automata and physical basis expressions and applying it to urban watersheds.
Lee, S., Choi, H., Woo, H., Noh, S. J., Lee, E. H., and Kim, S. H.
Proceedings of the Korean Society Of Hazard Mitigation (2023)

The effect of meteorological external force data on distributed hydrological simulation is evaluated, and the prediction accuracy of domestic and foreign meteorological external force data is investigated through data comparative analysis.
Kim, S., Kim, B., Lee, G., Lee, Y., Choi, J., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korean Society Of Hazard Mitigation (2023)

We compare and analyze the characteristics of daily hydrological simulations with ensemble-based sequential data assimilation techniques, ensemble Kalman filter, and particle filter techniques.
Lee, G., Kim, B., Lee, S., Oh, S., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korean Society Of Hazard Mitigation (2023)

A CADDIES-2D model based on cellular automata is applied to the Oncheon-cheon basin to verify the applicability of the model and assess the risk of flooding using a future climate change scenario.
Choi, H., Lee, S., Woo, H., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2022)

A high-resolution 100m water circulation analysis model based on WRF-Hydro was constructed for the Nakdonggang River basin and various spatial resolution combinations were simulated.
Kim, B., Kim, S. H., Lee, G., Lee, Y. W., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2022)

The CA prototype model is applied to slopes and test beds in urban areas to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of the model and verify its applicability.
Choi, H. J., Noh, S. J., Lee, E. H., and Kim, S. H.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2022)
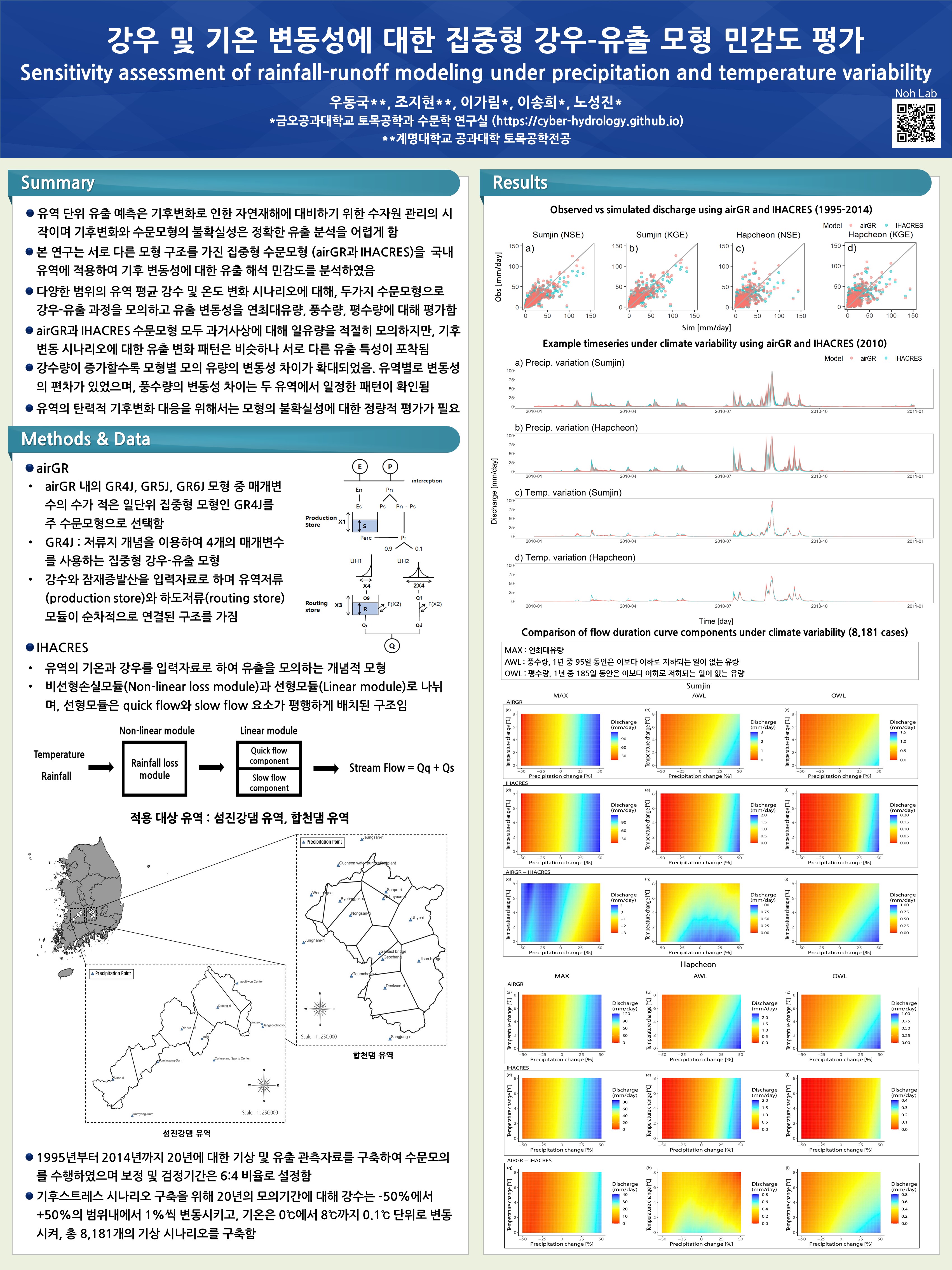
Analysis of the sensitivity of spillover analysis to climate variability by applying a centralized hydrological model (GR4J, IHACRES) with different model structures to domestic watersheds.
Woo, D. K., Jo, J., Lee, S., Lee, G., and Noh, S. J.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2022)

In order to examine the applicability of the urban flood simulation of the ensemble data fairy tale technique Particle Filter, a data fairy tale experiment based on virtual observation data was conducted.
Noh, S. J., Lee, S., Kim, B., Choi, H. J., Lee, G., and Lee, S.
Proceedings of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers (2021)
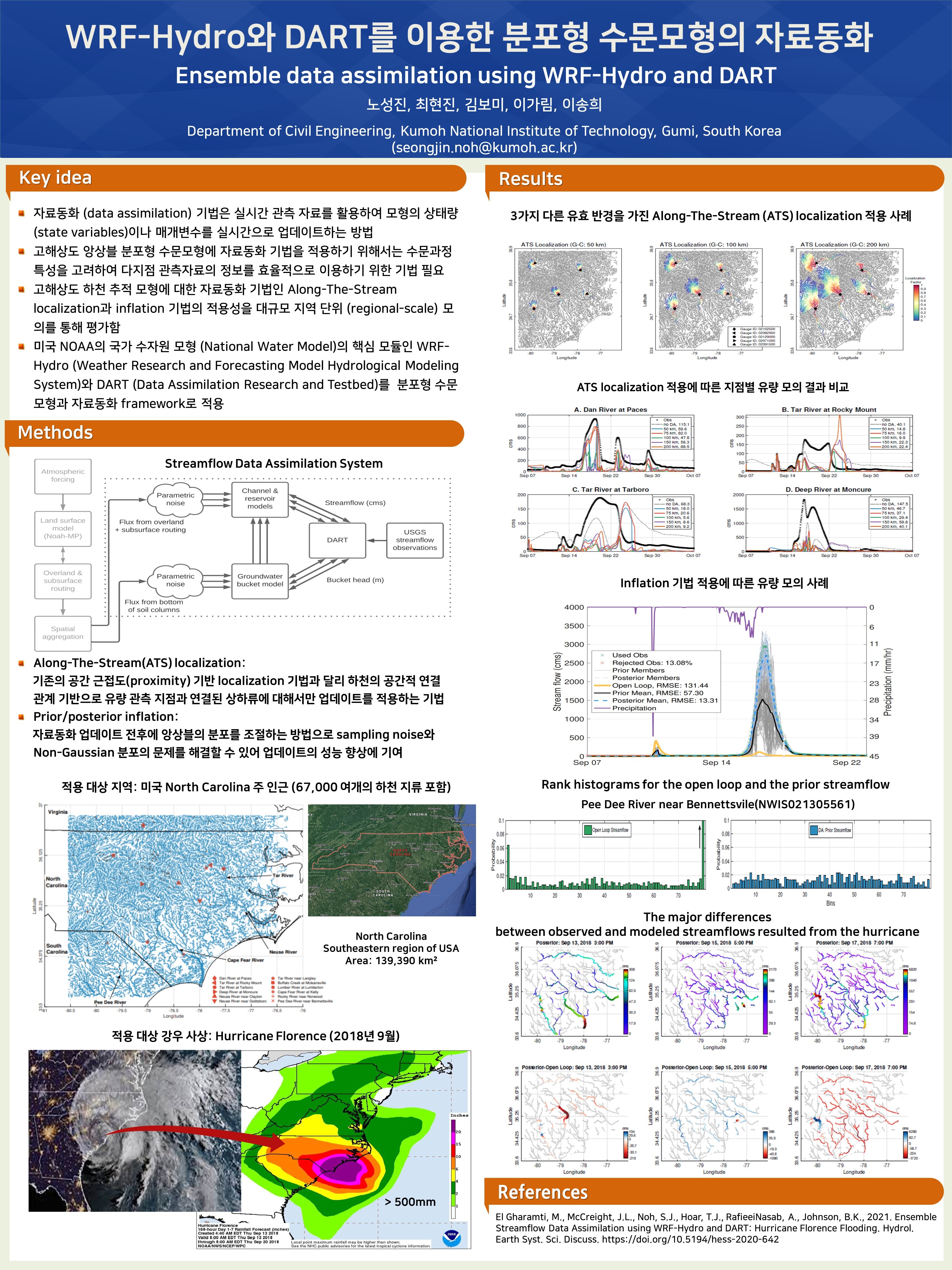
Using WRF-Hydro and DART, the distributed hydrological models, the applicability of Along-The-Stream localization and inflation data assimilation techniques was evaluated through large-scale regional simulation.
Noh, S. J., Choi, H. J., Kim, B., Lee, G., and Lee, S.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2021)

The characteristics of spatial resolution on flood analysis were analyzed using the integrated 1D-2D urban flood model, H12, and ultra-high resolution information.
Noh, S. J., Kim, B., Lee, S., Lee, J. H., and Choi, H. J.
Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference (2021)